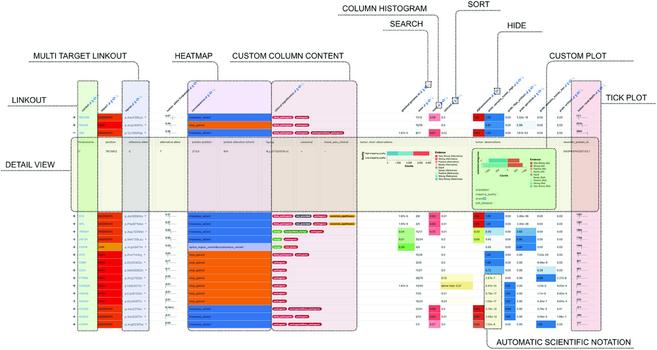
Why normalize databases?
Yesterday, my tutoring student asked me why databases need to be normalized at all. She said: “Wouldn’t it be easier to just have one big table with all the information?”
It’s a common first question when learning about relational databases.
At first, one big table (e.g. customer name, order date, product name, price) seems easiest.
I told her: Because that quickly leads to data redundancy, anomalies, and integrity issues when inserting, updating, or deleting records.
Because that quickly leads to data redundancy, anomalies, and integrity issues when inserting, updating, or deleting records. Normalization means structuring data into separate, related tables, so that each fact is stored only once. This reduces redundancy & preserves consistency.
Normalization means structuring data into separate, related tables, so that each fact is stored only once. This reduces redundancy & preserves consistency.



 AI底層數據建模
AI底層數據建模 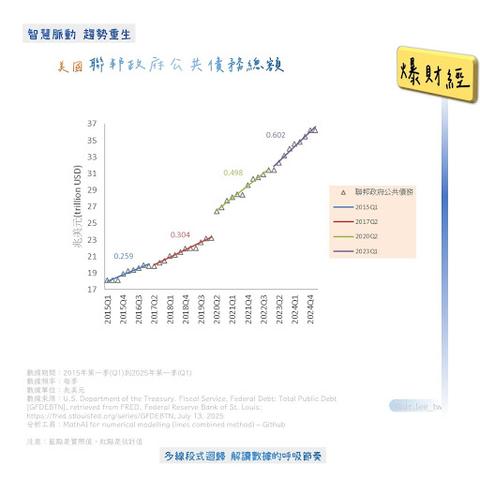


 :EA DATA. SF:
:EA DATA. SF: